Calculating Your Daily Energy Intake
Introduction
Whether your goal is to shed those extra pounds or pack on some healthy weight, understanding and calculating your daily calorie intake is the essential starting point. As previously discussed, a sustainable calorie deficit leads to weight loss, while adhering to a calorie surplus results in weight gain. But how do you accurately estimate your daily calorie needs? Enter the calorie calculator, a powerful tool that takes into account a multitude of factors to tailor your calorie intake to your unique requirements.
The Harris-Benedict Formula
To get a precise estimate of your daily calorie intake, we’ve developed our own calorie calculator based on the original Harris-Benedict formula. The Harris-Benedict equations, first published in 1918 and 1919, have served as foundational principles for calorie estimation.
Men: BMR = 66.5 + (13.76 × weight in kg) + (5.003 × height in cm) – (6.755 × age in years)
Women: BMR = 655 + (9.563 × weight in kg) + (1.850 × height in cm) – (4.676 × age in years)
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Even at rest, your body expends energy to maintain fundamental life-sustaining functions, including breathing, brain activity, circulation, nutrient processing, and cell production. This basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the baseline number of calories your body requires to carry out these vital functions.
Daily Calorie Needs
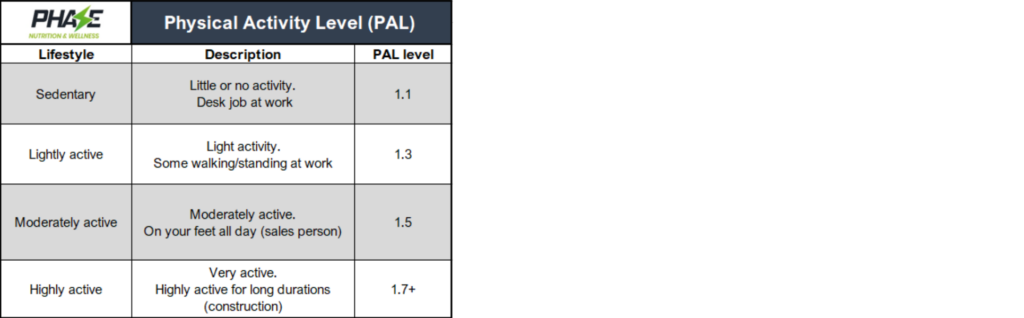
The next step in determining your daily calorie intake is to account for the calories burned during daily activities based on your lifestyle. This is where your Physical Activity Level (PAL) comes into play. It’s an estimate of your total energy expenditure over 24 hours based on your activity level:
- Sedentary: If you have minimal or no exercise, multiply your BMR by 1.1-1.2.
- Lightly active: If you engage in light exercise one to three days a week, multiply your BMR by 1.3-1.4.
- Moderately active: If you work out moderately three to five days a week, multiply your BMR by 1.5-1.6.
- Very active: For those who engage in intense exercise six to seven days a week, multiply your BMR by 1.7-1.8.
The resulting number represents approximately how many calories you need daily to maintain your current weight.
Calculating Your Daily Energy Intake
Here’s a step-by-step guide to calculating your daily energy intake:
Step 1: Calculate Your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Use our calorie calculator by inputting your details to determine your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR). BMR is the number of calories your body burns while performing its most fundamental life-sustaining functions.
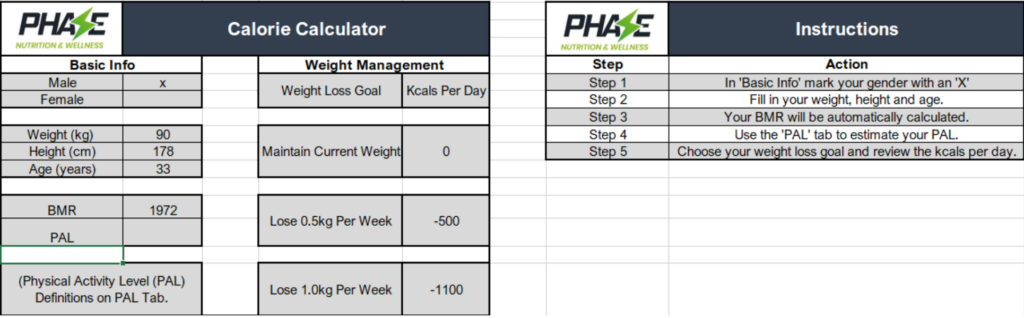
Step 2: Estimate Your Physical Activity Level (PAL)
Determine your estimated PAL, representing your total energy use over 24 hours, based on your daily activity.
Step 3: Calculate Your Total Daily Energy Intake (TDEE)
Input your estimated PAL into our calculator, which will then compute BMR × PAL, providing your Total Daily Energy Intake (TDEE).
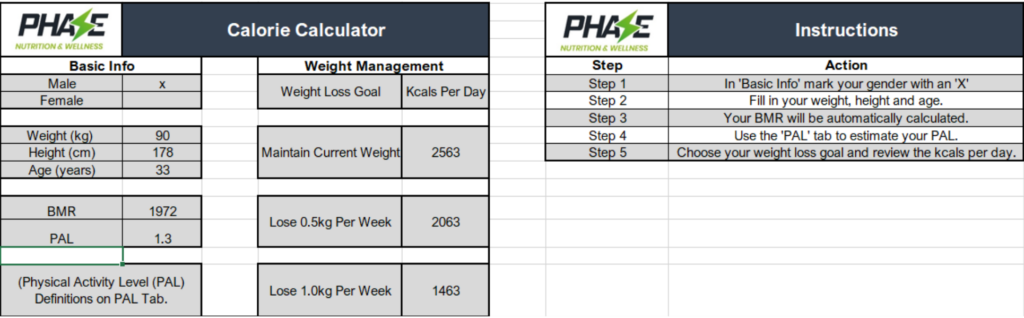
Note on Exercise
If you engage in additional exercise routines, you can include the calories burned during your workouts when estimating PAL. Simply add the calories burned to your recommended TDEE. For example, if your TDEE is 2,544 calories and you burn 300 calories during exercise, your maintenance calorie level would be 2,844 calories.
In summary, mastering the art of calorie calculation is fundamental to effective weight management. By understanding your BMR, PAL, and TDEE, you can tailor your daily calorie intake to support your specific goals, whether it’s losing weight, gaining weight, or maintaining a healthy balance. The calorie calculator is your key to unlocking a personalised approach to nutrition that optimally serves your body’s unique needs.
